Highly Safe Aqueous Rechargeable Batteries via Electrolyte Regeneration Using Pd–MnO2 Catalytic Cycle
- Year
- 2023
- Author
- Hyun-gi Jo, Eoyoon Lee, Seulki Han, Minji Jeong, Jinyeon Hwang, Hee-Dae Lim, Hyung-Seok Kim, Hyung Chul Ham, Si Hyoung Oh*
- Journal
- Energy Storage Materials
- Vol
- 61
- Page
- 102881
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2023.102881 1476회 연결
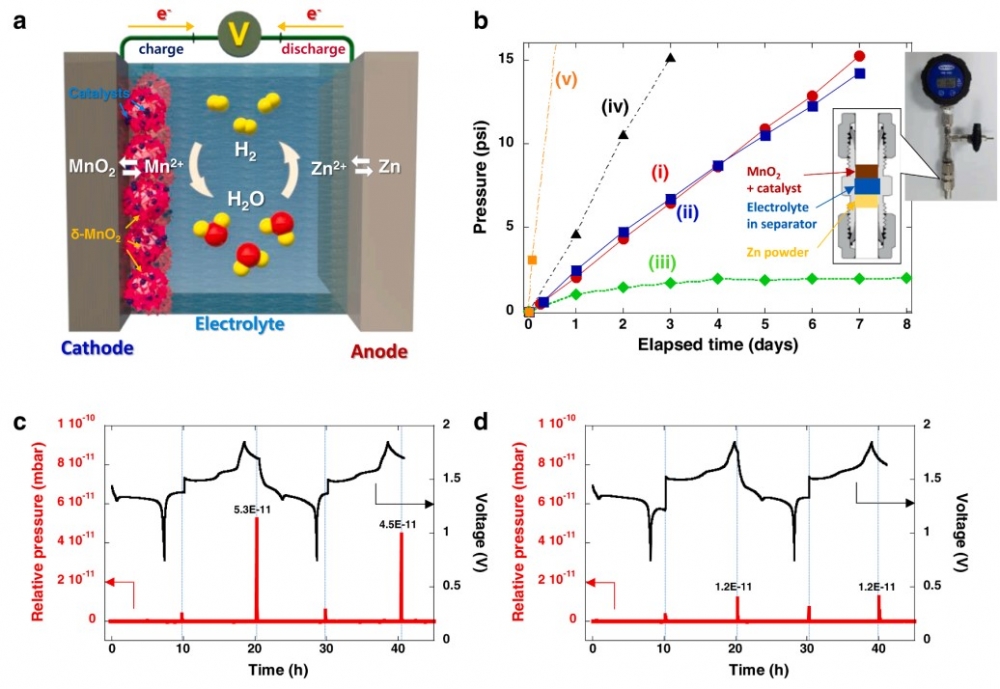
Long-term operation of aqueous Zn-ion batteries causes Zn metal corrosion at the anode due
to the thermodynamic instability of Zn in aqueous electrolytes, leading to significant hydrogen
(H2) accumulation, which seriously endangers battery safety. Herein, we propose a self-regulating battery based on internal electrolyte-regeneration mechanisms that control H2
production/annihilation reactions automatically and effectively suppress the pressure increase
and electrolyte depletion within the cell. This is accomplished by activating a water-regenerating chemical reaction between MnO2 on the cathode and H2 via a Pd catalyst, which
significantly relieves the reaction’s endothermicity. By electrochemically charging the cell, the
resultant Mn2+ and Zn2+ ions in the electrolyte can be easily reversed to their original chemical
states, i.e., MnO2 and Zn metal on the cathode and anode, respectively. This new strategy
overcomes the safety challenge posed by H2 accumulation, which is one of the key hurdles to
the commercialization of aqueous rechargeable batteries.