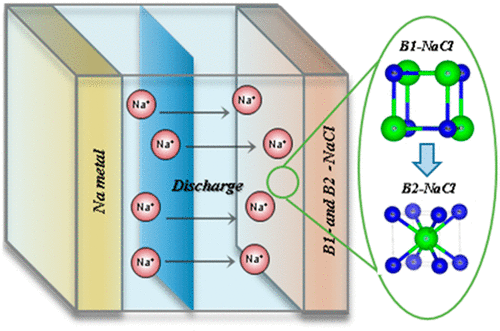
Sodium chloride (NaCl), a typical stoichiometric ionic compound, breaks all of the basic rules of chemistry at high pressures and can form new metallic compounds with different stoichiometries of NaxCl at x > 1. However, the electrochemical phase transition of NaCl from an insulating state to a metallic state without pressurization has not been achieved to date. In this study, we first demonstrate that nonmetallic NaCl can be transformed to a metallic compound through an electrochemical activation process. Subsequently, the activated NaCl electrode was shown to intercalate/deintercalate sodium ions into the structure, with a discharge capacity of 267 mAh/g by reversibly accommodating 0.6 Na ions. We believe that this method may represent a new approach for designing inexpensive electrode materials using the main component of table and sea salt for sodium-ion batteries. In addition, these results will contribute to the development of low-cost and sustainable rechargeable batteries that can be operated at a room temperature.
