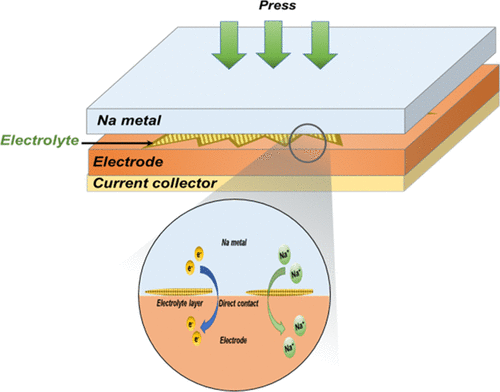
Most active materials for sodium-ion batteries suffer from the problem of low-energy efficiency in the first cycle because of the loss of active sodium ions consumed for the formation of a solid electrolyte interface. To make up for the lost sodium ion, presodiation treatments have been applied, which are effective ways to mitigate the low initial efficiency. Here, we developed a direct-contact method to achieve the presodiation for cathode and anode electrodes and demonstrated the enhanced Coulombic efficiency of the first cycle with improved cyclability and reversible capacity. Moreover, we proved the formation of a thick passivation layer at the cathode–electrolyte interface during the presodiation process; this contributes to the improved cycle stability by preventing the dissolution of the active material and its deposition on the anode surface. The direct-contact method is a simple and cost-effective way to complete presodiation, and this simple process will be widely applicable for practical battery manufacturing.
