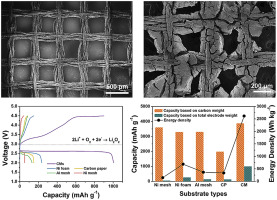
Li-O2 batteries have a high theoretical energy density; however, their current cathode system based on a heavy metal framework strikingly diminishes their real energy density. Herein, we report the fabrication of all-carbon-based cathodes composed of conventional active carbon and a carbon mesh (CM) framework produced from waste silk fabric by simple pyrolysis. CM frameworks show a high electrical conductivity of ∼150 S cm−1, good tensile strength of 34.1 ± 5.2 MPa, and a Young's modulus of 4.03 ± 0.7 GPa, as well as a well-ventilated ordered macroporous structure. These all-carbon-based cathodes exhibit stable cycling and high energy densities of ∼2600 Wh kg−1 based on total electrode weight, which are 4–15 times higher than those of conventional air cathodes.