High-performance thick cathode based on polyhydroxyalkanoate binder for Li metal batteries
- Year
- 2024
- Author
- Dong Hyuk Kang, Minhyuck Park, Jeonghun Lee, Chan Yeol Kim, Jimin Park, Youn-Ki Lee, Jong Chan Hyun, Son Ha, Jin Hwan Kwak, Juhee Yoon, Hyemin Kim, Hyun Soo Kim, Do Hyun Kim, Sangmin Kim, Ji Yong Park, Robin Jang, Seung Jae Yang, Hee-Dae Lim, Se Youn Cho, Hyoung-Joon Jin, Seungjin Lee, Yunil Hwang, Young Soo Yun*
- Journal
- Advanced Fiber Materials
- Vol
- 6
- Page
- 214
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00347-8 968회 연결
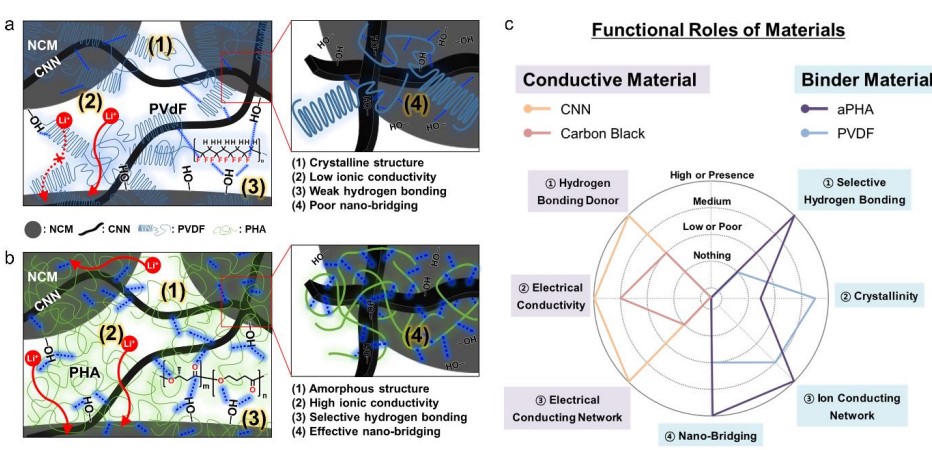
Thick cathodes can overcome the capacity limitations of conventional active cathode materials used in rechargeable Li batteries. However, the typical slurry-based method induces cracking and flaking during the fabrication of thick electrodes. In addition, a significant increase in the charge-transfer resistance and local current overload results in poor rate capabilities and cycling stabilities, thereby limiting electrode thickening. In this study, a synergistic dual-network combination strategy based on a conductive nanofibrillar network (CNN) and a nanobridging amorphous polyhydroxyalkanoate (aPHA) binder was used to demonstrate the feasibility of constructing a high-performance thick cathode. The CNN and aPHA dual network facilitates the fabrication of a thick cathode (≥ 250 μm thickness and ≥ 90 wt.% active cathode material) by a mass-producible slurry method. The thick cathode exhibited a high rate capability and excellent cycling stability. In addition, the thick cathode and thin Li metal anode pair (Li//t-NCM) exhibited an optimal energy performance, affording high-performance Li metal batteries with a high areal energy of ~25.3 mW h cm−2 , a high volumetric power density of ~1,720 W L−1 , and an outstanding specific energy of ~470 W h kg−1 at only 6 mA h cm−2 .